
Finally, we find the final velocity of the object from the momentum change. First, we find the total impulse with the help of graph given above then total impulse gives us the momentum change. Second.Īrea under the graph gives us impulse. If a force is applied to this object between (1-7) seconds find the velocity of the object at 7. time graphs of the system are similar because momentum is directly proportional to the velocity.Įxample: The graph given below belongs to an object having mass 2kg and velocity 10m/s. We can also draw momentum versus time and velocity versus time graph of the system.Īs you can see momentum vs. Total impulse gives us the change in momentum as we said before.
As shown in the graph, A1 is positive impulse and A2 is negative impulse. Since impulse is equal to the multiplication of force and time then, area under this graph also gives us impulse. Look at the given graph below that shows the relationship of the force and time of a given system. In this unit we will again benefit from the graphs. On the contrary if you want big force then you should decrease the time and you get big force. Thus, the unwanted results of force can be eliminated by increasing the time of force application. As you see increasing the time decreases the amount of force. Then you push it with a 5N force for 4 seconds and impulse does not change. Assume that, you push a box with a force of 10N for 2 seconds, the impulse is 20N.s. For example, in collisions like car crash or any other collision we can calculate the affect of force by controlling the time. We experience the results of impulse and momentum in daily life.

In examples we will benefit from this equation.Įxample: If the time of force application is 5s find the impulse of the box given below.Įxample: Find applied force which makes 10m/s change in the velocity of the box in 5s if the mass of the box is 4kg.į.t=4kg.10m/s=40kg.m/s Impulse of the box is 40kgm/s Let’s find this relation now.Īs you can see, we found that impulse is equal to the change in momentum. Impulse and momentum are directly related to each other. It has the same direction with applied net force. Impulse is also a vector quantity having both magnitude and direction. In summary, I try to say that impulse is the multiplication of applied force and time interval it applied. However, if you apply force on an object long period of time then you see the amount of change in momentum is bigger than the first situation. If you apply a force on an object 1 s then you see small change in the momentum. How long does it act on an object? It is linearly proportional to the change in velocity.
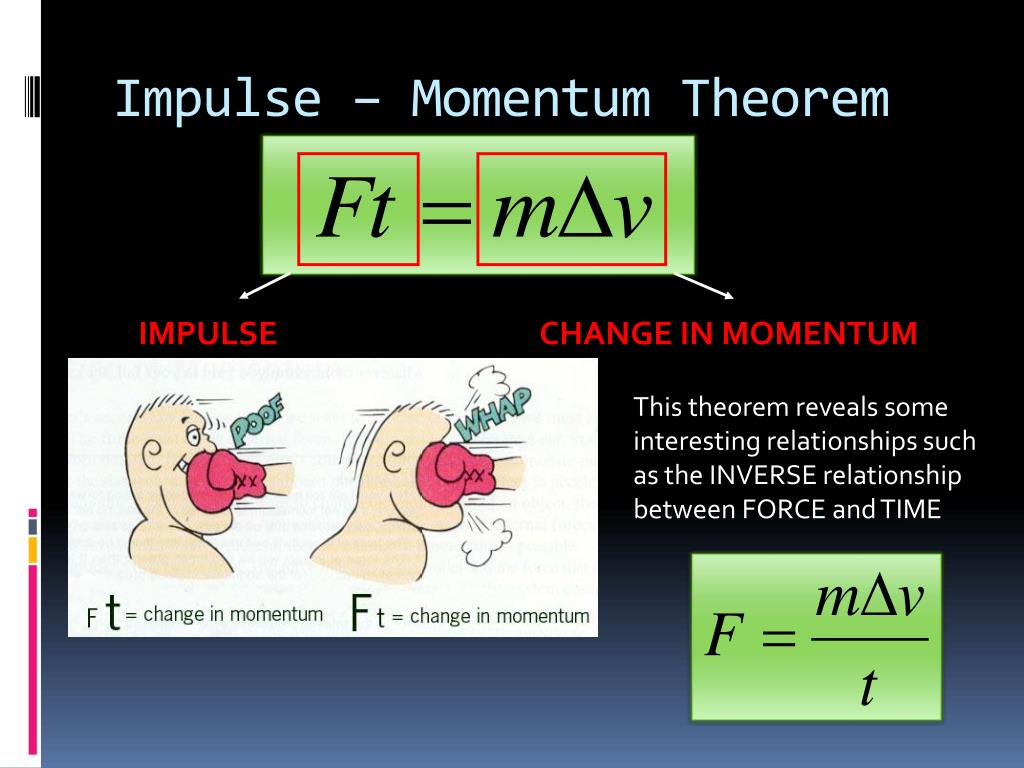
Another important thing is the time of applied force. Change in the velocity is proportional to the applied net force. In the first unit we said that force causes acceleration in other words change in the velocity is the result of applied net force. The name unit comes from the integral of the force over time t, which results in the unit change of the linear momentum I: (1. If velocity changes then acceleration occurs. (1.76) which is zero for all values of t, except at, as the amplitude goes to infinity. In most of the case mass is constant and for momentum change velocity changes. We discussed above the factors changing momentum which are mass and velocity.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
